Have you ever wondered how leading products came to life? From the latest apps to cutting-edge software, everything begins with an idea. But there’s a journey from that initial spark to a product hitting the market. This journey is known as the new product development process.
New product development (NPD) is about creating or significantly improving existing products. It’s not just about having a great idea. It involves understanding customer needs and designing a product to meet those needs. Then, it’s about carefully planning how to bring it to market. Think of it as a bridge that turns raw concepts into real marketable products.
Why prioritize NPD? It’s simple: innovation drives success. NPD empowers businesses to adapt to market shifts, meet evolving customer needs, and stay ahead of competitors. It’s a cornerstone for growth and sustainability, from startups to established corporations.
Mastering NPD is essential for the growth and survival of startups and large companies.
In this article, we’ll dive into the essentials of the new product development process. We’ll explore each step that helps transform a product concept into a successful tool.
Understanding the new product development process
At its core, new product development is about bringing solutions to life. A product development team turns a product concept into a tangible solution. But why is it so crucial for businesses? The answer lies in three key areas: innovation, competition, and customer needs.
Innovation
NPD is the fuel for innovation. It drives businesses to explore new possibilities. As a result, they create products that open up fresh markets or enhance their presence in existing ones.
Competition
New products are popping up all the time, almost in every market. Staying competitive means continuously evolving. NPD keeps businesses at the forefront of change, ensuring they don’t fall behind.
Customer needs
Customer preferences are always changing. NPD helps businesses stay relevant. It encourages companies to evolve their products to meet these changing needs. This ensures long-term customer loyalty.
Example: Salesforce
Salesforce stands out in how it uses customer feedback. They regularly update their CRM system based on what users say. A key update was the introduction of the Lightning Experience – a more intuitive user interface. This change came after users asked for a simpler and more efficient way to manage their sales data
Main steps of the process
The new product development process can be complex. It generally follows these main steps:
- Ideation and idea screening
- Feasibility analysis and market research
- Design and development
- Product planning and implementation
- Marketing strategy development
- Launch
- Feedback and iteration
Each step is essential in creating a product that meets the market need and excels in the competitive landscape. Let’s delve deeper into each development phase. We’ll explore the best practices and strategies that lead to successful new product development. Follow along!
Ideation
The ideation phase is where creativity blooms. Here are some methods to generate and manage product ideas.
Brainstorming
You’ve heard of this classic technique. You gather a team and encourage a free flow of ideas without immediate criticism or analysis. The goal is to generate many ideas, fostering creativity and out-of-the-box thinking. A new idea can come easier when there’s no judgment.
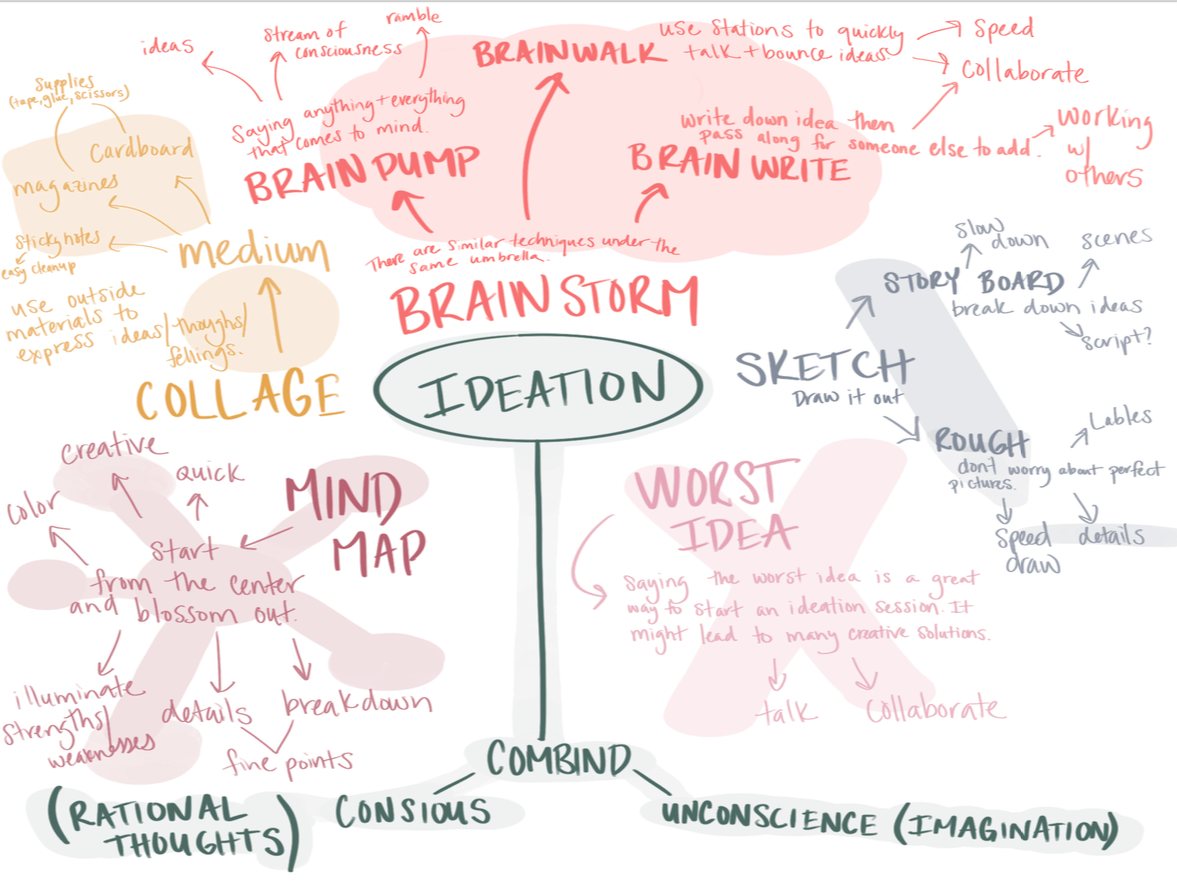
Reverse brainstorming
This method turns traditional brainstorming on its head. You focus on problems instead of solutions. The team identifies potential issues or challenges. Then, you brainstorm ways to resolve these problems, leading to innovative solutions. It’s less about a new idea and more about an immediate issue to solve.
Idea mapping
This visual technique involves creating a diagram showing the relationship between ideas. Some people call this “mind mapping.” It starts with a central concept. Then, related ideas branch out. This helps to organize thoughts and spot connections.
SCAMPER
This acronym stands for:
- Substitute
- Combine
- Adapt
- Modify
- Put to other uses
- Eliminate
- Reverse
It prompts teams to look at a product or service differently, leading to unique ideas. For example, it can get you thinking about combining or modifying different components. You can also explore alternative uses of your product here.

Five “Whys”
A technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. Asking ‘why’ multiple times (typically five) helps in drilling down to the root cause of a problem. This often leads to innovative solutions that address the core issue.
Try using a combination of these methods to find what works for you. There’s no universal “best practice” that works for everyone.
Now that your product team has generated lots of ideas, how do you choose the best ones?
Evaluating potential ideas
It’s essential to evaluate ideas critically. This evaluation involves assessing each idea’s feasibility, scalability, and potential market impact. Ask yourself – is this new product idea:
- Solving a real problem
- Technically and financially viable
- In alignment with the company’s goals and values
Tools like SWOT analysis can be instrumental in this phase. Let’s run through this technique.
SWOT analysis
| Strengths Focus on the internal, positive attributes of the idea or project Include resources, capabilities, or any advantages the company has over competitors | Weaknesses Identify internal limitations Find areas where the idea or project may be lacking compared to competitors |
| Opportunities External factors that the idea or project could exploit to its advantage Market trends Regulatory changes Technological advancements | Threats External challenges that might pose a risk to the success of the idea Competition Market volatility Changing consumer preferences |
All that sounds like a lot of work! But don’t try to do it all alone. Involve key team members to help you.
Who should be involved
Ideation is most effective when it involves a diverse group of people. This includes team members from various departments:
- Product managers
- Marketing
- Design
- Engineering/software development
- Sales
- Select customers
- External experts
The key is to create an environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing and building on ideas.
Real-world example: Netflix
Netflix’s shift from DVD rentals to streaming services showcases successful ideation and evaluation. Netflix was first a DVD rental service. They identified the growing trend in streaming and pivoted their business model just in time.
It didn’t just happen though. They performed a thorough market analysis and explored changing consumer preferences in-depth.
They also carefully evaluated different ideas and decided to produce original content. As we all know, it’s been a major success.
This is how you can fuel your business strategy with innovative ideation and meticulous evaluation.
Feasibility analysis and market research
Before diving into product development, conduct a thorough feasibility analysis and market research. This stage is all about ensuring your product idea is viable and resonates with your target audience.
Understanding your market through research
This step involves analyzing:
- The target audience
- Current market trends
- Competitor strategies
- Potential demand for the product
How can you do that? There are a few ways.
Data collection methods
Data collection for market research can take many forms:
- Surveys and questionnaires: gathering quantitative data from a large audience
- Interviews: conducting one-on-one discussions for qualitative insights
- Focus groups: facilitating group discussions to explore consumer opinions and attitudes
- Observational research: studying consumer behavior in natural settings
- Secondary research: analyzing existing data from reports, studies, and other sources
Once again, no single method is the best. A combination of these methods often yields the best results.
Here are a few more interesting ones.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
QFD translates customer needs into specific technical requirements and operational plans. It focuses on “the voice of the customer.” By using QFD, teams can:
- Prioritize product features based on customer desires
- Systematically transform these desires into design targets
- Identifying and defining product attributes that appeal to consumers
You need to go beyond the basic customer needs. Dig into the more subtle preferences and customer expectations.
Try the following techniques:
Understanding these attributes ensures the final product resonates with and satisfies consumer expectations.
The outcome of a feasibility study helps decision-makers determine what to do:
- Proceed with the project
- Modify the approach
- Abandon the idea
Example: Airbnb
Airbnb expanded from offering just accommodations to unique travel experiences. Now you can book cooking classes and guided tours through Airbnb. This shift came in response to a growing consumer desire for authentic, local experiences.
By this point, you’ve done lots of research. It’s time to start thinking of your actual product.
Design and development
This is where your product starts to take shape. Remember – you’re not creating the final product just yet. Instead, you’re preparing a version for concept testing.
Importance of design thinking and iterative development
Design thinking focuses on understanding users. It’s about creatively solving their problems.
Iterative development means you improve the product step by step. You build, get feedback, and then improve. This approach helps make products that people really want and need.
Keep these in mind as you start product design.
Double diamond process
The double diamond process includes the following:
- Discover and research the problem
- Define it clearly
- Develop solutions
- Deliver the product
Prototyping
Making a prototype is like creating a rough draft of your product. Some people call this concept development. It’s not final, but it helps you understand how your idea works in the real world. It’s a practical way to explore and refine your product.
User feedback
Feedback from users is super valuable, especially here. You might wonder: “My product isn’t live yet. How can I get feedback?”
You can:
- Find beta testers
- Research feedback for competing products
- Use feedback from a previous product you developed
User feedback tells you what works and what doesn’t. Use these insights to make your product better.
Testing
Testing is all about making sure your product works well. It includes checking for bugs and seeing how users interact with it. Good concept testing helps ensure your product is ready for the market.
Example: Spotify
Spotify’s data-driven approach to feature development has been pivotal in its success. They continuously analyzed user behavior and preferences through data analytics. Result? Personalized features like Discover Weekly and Spotify Wrapped. These features enhance user experience. They also foster a deeper connection with the platform. This is the true power of data in driving innovative product development.
Product planning and implementation
It’s time to actually create your product! Here’s how.
Understand market needs
If you’ve been following along, you’ve done a lot of research already. Still, it’s important to reiterate this point.
Deeply understanding your customers is critical. This involves more than just knowing their basic requirements. It’s about delving into their behavior, preferences, and unmet needs. You can try:
- Conducting market research
- Analyzing customer feedback
- Observing how they interact with current products
This understanding helps create a product that meets and exceeds customer expectations.
Identify gaps in existing solutions
Carefully analyze the current market offerings. Look for what they lack or where they fall short in meeting customer needs. Your product can address these shortcomings, offering better solutions or filling unmet needs. Try to add real value where competitors are lacking.
Forecast future market trends
Stay ahead of the curve by predicting future trends. Analyze current market dynamics, emerging technologies, and shifting consumer behaviors. You’ll be able to forecast where the market is heading.
Define a clear value proposition
Articulate what sets your product apart. This goes beyond just listing features. Ask yourself:
- How does it solve problems better?
- Why should customers choose it over others?
A strong value proposition is clear, compelling, and directly addresses the needs and wants of your target market.
Prioritize features
There are lots of prioritization methods. Here are some of the most common ones:
- MoSCoW method: categorizes features into Must-haves, Should-haves, Could-haves, and Won’t-haves. It helps in understanding the criticality of each feature.
- Kano model: classifies features based on customer satisfaction. Categories include:
- Delightful
- Expected
- Indifferent
- Value vs. complexity matrix: compares the value to the customer against the complexity of implementing a feature. It helps in identifying high-value, low-complexity features for early release.
- 100-dollar test (cumulative voting): stakeholders are given a hypothetical $100 to ‘spend’ on features. How stakeholders allocate their budget signals how important each feature is.
- Story mapping: creates a visual map that lays out the user journey and plots features against this journey. It’s great for understanding how features fit into the overall user experience.
These methods offer different perspectives on feature prioritization. Try a few of these and see which method is best for you. It may vary from project to project, so keep them all in mind.
Check out Canny’s roadmap prioritization software to make prioritization a breeze.
We’ve compiled the best prioritization techniques in this free guide. Get it here and learn more about prioritization.
Example: Asana
Asana is a great example of smart feature prioritization. They faced a challenge: their users were from diverse industries, each needing different things. So, Asana used the MoSCoW method. They categorized features into ‘Must-haves’ and ‘Nice-to-haves.’ This helped them focus on essential features first (like task assignments and progress tracking). This way, the tool remained useful for a broad user base.
Design with users in mind
Focus on creating an intuitive and easy-to-use design. This is called a “user-centric approach.” You need to understand the user’s journey and design a seamless and engaging experience for them.
This involves:
- Feedback collection
- User testing
- Empathy for the user’s experience
- Ensuring the design is equally attractive and functional
Plan for scaling and flexibility
Plan your product with growth in mind. Ensure that your product can scale effectively as user numbers increase. Additionally, keep your design flexible. This will help you adapt to market changes, user feedback, and new opportunities.
Implement security measures
Enforce strong security measures to protect user data and build trust. This is particularly crucial for digital products. Data breaches can have significant consequences. Consider the following:
- Data encryption
- Secure authentication
- Regular security audits
Develop a minimum viable product (MVP)
Start with developing an MVP. This version should include just enough features to be functional and provide value. This way, you can enter the market quickly and start gathering user feedback. An MVP approach helps test your product idea in the real world and iteratively improve it.
Adopt Agile methodologies
Adopt Agile development practices for more efficient and flexible product development. Agile teams are known to rapidly adapt to feedback and changes. New product introduction can benefit from this.
Make decisions with data
Base your decisions on data and analytics. Track and analyze:
- How users interact with your product
- What features they use the most
- Where they face issues
This data-driven approach helps make informed decisions about product improvements and marketing strategies.
Think about marketing
Develop a marketing strategy that specifically targets your audience. Identify the most effective channels and messaging to reach your target market. A focused approach helps here. It ensures that your marketing efforts resonate with your potential customers. We’ll talk more about marketing later in the article.
Add customer support and education
Establish robust customer support systems. Provide resources like tutorials, FAQs, and help centers to educate users about your product. Good customer support enhances user experience and significantly impacts customer satisfaction and retention.
Determine pricing
Create a competitive and flexible pricing strategy. Consider different pricing tiers to cater to various user needs and preferences. Offering options like free trials can attract users to try your product. Consider running product pricing experiments to perfect your pricing.
Consider compliance and legal aspects
Ensure your product complies with all relevant laws and regulations. Staying compliant is crucial for operating legally and maintaining user trust. Regulations like GDPR are top of mind for many SaaS companies right now.
Iterate
Continue to develop and improve your product based on user feedback and market trends. Here are some more ideas to consider.
Product readiness assessment tools. Evaluate how ready your product is for the market. You need to understand the product’s maturity and how prepared it is for customer use.
- Technology Readiness Level (TRL). Assess the maturity level of your product’s technology. How developed is the technology? What needs to be improved for successful market adoption? This technique might help answer those questions.
- Investment Readiness Level (IRL). Evaluate your product’s attractiveness to investors with IRL. How prepared is your product for investment? How viable is your business model? What’s the market potential?
This ongoing iteration process is crucial. It ensures your product stays relevant, competitive, and continually meets user needs.
Remember: it’s a mistake to assume you already have the final product. A good product keeps evolving.
Example: Zoom
Zoom’s response during the COVID-19 pandemic is a textbook case of rapid iteration. Everyone was faced with unprecedented demand and new security challenges. Zoom quickly implemented enhanced security features and expanded its server capacity. This showed agility in addressing user feedback. They quickly adapted to a changing market environment and grew when everyone else was struggling.
This was an overview of everything in the new product development process. Let’s talk more about bringing it to the market.
Marketing strategy for new products
You may have a great product. But how will people learn about it? This is where marketing comes in.
Your marketing team will likely take care of this. However, knowing what’s involved will help product managers understand the entire process better.
Understanding the market
Start by gaining a deep understanding of the market landscape. This involves studying industry trends, consumer behaviors, and market dynamics. Look for emerging patterns and shifts that could impact your product’s success.
Researching competition
Analyze your competitors thoroughly. Understand their products, marketing strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. This insight helps you find opportunities to differentiate your product and uniquely position it in the market.
Finding your target audience
Identify who will benefit most from your product. Analyze demographic data, interests, and behaviors to pinpoint your ideal customer base.
Developing user personas
Create detailed user personas representing your target audience. These personas should include demographics, interests, pain points, and motivations. They guide your marketing messages and strategies.
Crafting your unique selling proposition (USP)
Define what sets your product apart. Your USP should clearly articulate your product’s unique benefits and value to the customer.
If you’re launching a new project management software, your USP could be:
“Revolutionizing team collaboration with AI-driven task prioritization.”
This USP highlights the unique feature of AI-driven task management. It sets the software apart. That’s because it offers a specific and innovative solution to a common challenge in project management.
A value proposition is another way of looking at this. Explore more about value propositions here.
Creating compelling messages
Develop messaging that resonates with your target audience. Your messages should align with your USP and effectively communicate the benefits of your product.
Determining optimal channels
Choose the best channels to reach your audience. Consider:
- Social media
- Digital advertising
- Email marketing
- Traditional media
How do you pick? Choose based on where your audience is most active. Test marketing is the key here – experiment and see what works best for your unique product and audience.
Launching the product
Plan a product launch strategy that makes an impact. Think about:
- Launch events
- Influencer collaborations
- Digital campaigns
The goal is to create buzz around your product.
Promotion: grabbing their attention
Think of what promotional tactics could make sense. Discounts or limited-time offers can attract and retain customer attention.
Evaluating
After launching, assess the effectiveness of your marketing strategy. Analyze metrics and feedback to understand what worked well and what can be improved for future campaigns.
Let’s talk more about evaluating your marketing success and overall new product development.
Measuring and iterating
This process is crucial. Many companies are just happy to release the product into the world and exhale. But you can’t move forward unless you know what’s worked and hasn’t.
Here’s how you can evaluate the effectiveness of your efforts. Don’t skip this step!
Customer feedback and market trends. Regularly collect and analyze customer feedback. Monitor market trends to stay updated on changing consumer preferences and industry shifts. This information is vital for making data-driven improvements to your product.
Lean Startup methodology. Embrace the approach of ‘build-measure-learn.’ This involves introducing changes, measuring their impact, and learning from the results. It’s a cycle of continuous improvement based on real-world data.
Example: Dropbox
Initially, Dropbox released a beta version to gather user feedback. This was crucial in refining their file-sharing service. Their unique referral program offered additional free storage space for both the referrer and the referee. That significantly boosted their user base.
Conclusion: how to make new products successful
Success in new product development hinges on several key factors:
- Deep market and customer insight. Knowing your audience and market trends is foundational. Without this, even the most innovative products may miss the mark.
- Continuous idea generation. Innovation starts with great ideas. Cultivating an environment where creativity flourishes is essential.
- Iterative development. Product development is not a one-time effort but a continuous cycle of improvement. Implementing Agile methodologies ensures your product evolves rapidly to meet changing user needs.
- Customer feedback integration. Your users are your best critics. Incorporating their feedback ensures your product not only meets but exceeds their expectations.
- Unique selling proposition (USP). In a crowded market, your product needs to stand out. A strong USP will set your product apart and define its place in the competitive landscape.
- Adaptability and flexibility. The ability to quickly respond to market changes and emerging trends is crucial. Staying flexible and ready to pivot based on user feedback and new insights ensures long-term relevance and success.
You need to quickly respond to market changes and emerging trends. You also have to listen to user feedback. That’s how you can ensure your product stays relevant and successful. We’ve discussed lots of frameworks that can help you stay on top of all this.
We’re excited to see what new products you bring to the market! Canny can help you collect, manage, and analyze feedback for those invaluable insights. Give it a try today!







